In this article
- What is the Asset Lifecycle?
- Exploring 5 Key Stages of the Asset Lifecycle
- Financial Considerations in Asset Lifecycle Management
- Technology Integration for Finance Control
- Why are Asset Lifecycle Stages Needed?
- Strategies to Prolong Asset Life
- 5 Key Strategies to Prolong your Asset Life
- Effective Asset Life Cycle Management
- Maximize your Asset Lifecycles with Asset Management Software
In this article
- What is the Asset Lifecycle?
- Exploring 5 Key Stages of the Asset Lifecycle
- Financial Considerations in Asset Lifecycle Management
- Technology Integration for Finance Control
- Why are Asset Lifecycle Stages Needed?
- Strategies to Prolong Asset Life
- 5 Key Strategies to Prolong your Asset Life
- Effective Asset Life Cycle Management
- Maximize your Asset Lifecycles with Asset Management Software
Managing your fixed asset lifecycle journey from investment to replacement is crucial to long-term success. Effectively navigating each stage of the lifecycle can optimize resources, enhance operating efficiency, and maximize your return on investment. Here we address best practices for managing the lifecycle of an asset, from initial creation to ultimate disposal. With effective planning and control, organizations can prolong the useful life of fixed assets and derive maximum value from these investments.
All organizations must make long-term capital investments for growth. These assets may be tangible plant and equipment, or intangible software. Regardless of their nature, every asset has a lifecycle that demands careful attention. Managing these assets effectively is vital to strategic success.
The asset lifecycle provides a roadmap for fixed asset management. Best-practice strategies at each stage of the asset lifecycle maximize asset value.
What is the Asset Lifecycle?
The asset lifecycle refers to the stages that an asset goes through from initial planning and acquisition to its eventual disposal. Assets produce future economic benefits and may be physical or intangible. Each stage of the asset lifecycle involves certain activities, decisions, and considerations.
Asset lifecycle management addresses each stage of an asset’s life so that well-informed decisions are made. This achieves operating efficiency and maximizes the opportunity for a greater return on investment.
Exploring 5 Key Stages of the Asset Lifecycle
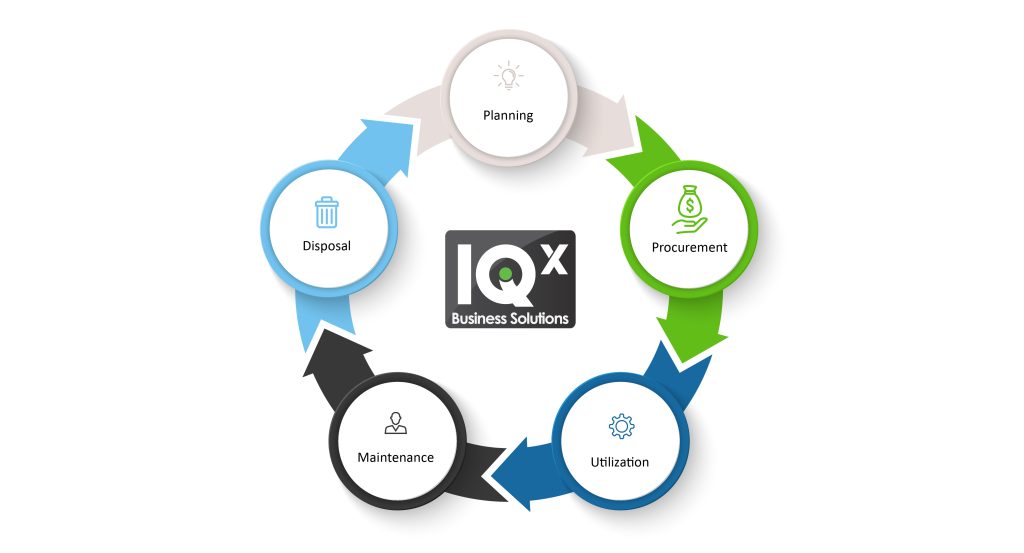
1) Planning
During the planning stage, organizations identify their requirement for new assets to meet their strategic goals.
The need for new assets stems from new business requirements, new technologies, or replacement of obsolete assets. During this phase, a budget is prepared to acquire these assets.
Planning and selection of assets is a critical step as this is the foundation of the entire lifecycle.
2) Procurement
This stage involves researching potential suppliers, sourcing of the assets, gaining the approvals needed and the negotiation of contracts. The procurement team will decide whether to purchase or lease the required assets.
3) Utilization
During this phase, assets are placed into active use to fulfill their operational purpose. The assets are integrated into existing systems or processes. The duration and value derived from these assets will depend on how well they are managed.
4) Maintenance
Maintain assets regularly to extend their useful life. A maintenance strategy helps ensure that upgrades or refurbishments are conducted to optimize asset efficacy. Monitor assets to identify operating issues that you can address promptly.
5) Disposal
At the end of the useful life of the asset, it is retired or disposed. This may be when they are no longer cost-effective, and where retaining them will be more costly than the income they generate. The disposal or retirement of an asset should be carefully planned as it will likely require replacement, which may require some time to complete.
Financial Considerations in Asset Lifecycle Management
1) Capital Budgeting Techniques
Finance executives play a pivotal role in steering organizations through the intricacies of the asset lifecycle. At each stage, employing judicious capital budgeting techniques becomes paramount for informed decision-making.
Net Present Value (NPV): NPV is a fundamental tool used to assess the present value of future cash flows associated with an asset. By discounting future cash flows back to their current value, NPV aids in determining the financial viability of acquiring or investing in assets.
Internal Rate of Return (IRR): IRR measures the profitability of an investment by calculating the rate of return that equates the present value of cash inflows with the present value of cash outflows. This technique evaluates the attractiveness of an asset over its lifecycle.
Payback Period Analysis: Payback Period is a straightforward metric that indicates the time required for an investment to recoup its initial cost. This technique provides insights into the timeframe within which an asset is expected to generate positive cash flows.
By employing these techniques at different stages of the asset lifecycle, finance executives can thoroughly evaluate the financial implications of acquiring, maintaining, or disposing of assets, ensuring alignment with organizational goals and financial objectives.
2) Risk Management in Asset Lifecycle
Navigating the asset lifecycle is not without its financial risks. Finance executives must adeptly identify and manage these risks to safeguard the organization’s financial health.
Insurance Coverage: Mitigating risks through comprehensive insurance coverage is a proactive strategy. This ensures that potential losses associated with asset-related risks are covered, minimizing financial impact in the event of unforeseen circumstances.
Contingency Planning: Developing robust contingency plans is essential. By strategizing and preparing for potential financial setbacks, an organization can ensure its resilience in the face of uncertainties that may arise during the asset lifecycle.
Financial Modelling: Leveraging advanced financial modelling techniques enables finance controllers to simulate various scenarios, assessing potential financial impacts. This foresight aids in strategic decision-making, allowing the organization to proactively address and mitigate financial risks.
3) Budget Allocation and Resource Optimization
Effective asset lifecycle management is a linchpin in achieving optimal budget allocation and resource utilization. Finance executives can strategically align budgetary priorities with the critical stages of the asset lifecycle, ensuring efficiency and fiscal prudence.
By integrating asset lifecycle considerations into budgetary planning, finance executives can allocate resources judiciously, addressing the specific needs of each stage—from acquisition planning to disposal. This approach optimizes the organization’s financial resources, fostering a more resilient and adaptable financial structure.
Technology Integration for Finance Control
The integration of cutting-edge asset management solutions emerges as a strategic imperative for finance executives. Modern organizations recognize the pivotal role of technology in fortifying financial control systems. Seamless integration of fixed asset management systems is a critical component of an effective digital transformation strategy.
1) Importance of Integration
The integration of Fixed Asset Management Software into financial control systems is a transformative step towards enhancing efficiency and precision throughout the asset lifecycle. This integration facilitates a unified platform that delivers comprehensive insights, real-time monitoring capabilities, and advanced analytics, thereby generating confident decision-making confidence.
2) AI-Driven Platforms
The advent of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has further elevated the capabilities of asset management software by providing intelligent automation, predictive analytics, and data-driven insights. These sophisticated tools not only streamline routine processes but also contribute to proactive decision-making by anticipating trends and potential issues in the asset lifecycle.
3) Real-Time Monitoring
Fixed Asset Management Software offers the invaluable capability of real-time monitoring. This provides visibility into the status and performance of fixed assets, allowing for timely interventions, preventive maintenance, and rapid responses to emerging challenges. Real-time monitoring minimizes the risk of operational disruptions and enhances overall asset efficiency.
4) Financial Reporting Excellence
Integrating Fixed Asset Management Software into financial control systems significantly improves the accuracy and efficiency of financial reporting. By automating the tracking of asset-related financial data, organizations can ensure compliance with accounting standards, reduce the risk of errors, and expedite the reporting process. This not only enhances financial transparency but also aids in strategic planning and budgetary decision-making.
5) Predictive Analytics for Informed Decision-Making
The incorporation of AI-driven predictive analytics within fixed asset management software empowers finance executives to foresee potential issues and trends in the asset lifecycle. By analyzing historical data and identifying patterns, these platforms assist in making informed decisions regarding maintenance schedules, asset upgrades, and overall financial planning. This proactive approach mitigates risks and contributes to long-term financial sustainability.
Why are Asset Lifecycle Stages Needed?
The asset life cycle stages provide a framework for managing assets effectively, which ensures their contribution to the organization is maximized throughout the lifecycle. The specifics of each phase will vary from one organization to another, depending on the nature of the industry.
Asset lifecycle management in tandem with capital project management is vital in addressing each of the asset’s lifecycle stages effectively and extending the assets’ usability without diminishing the functionality of the asset.
Effective asset lifecycle management helps organizations make informed decisions about when to invest in new assets, how to maintain the existing assets and when to dispose or replace aging assets. The prolonging of the asset lifecycle is imperative in maximizing their value and return on investment.
Strategies to Prolong Asset Life
Prolonging asset life maximizes return on investment and has a significant impact on capital budgeting techniques and resource allocation. Reducing capital expenditure, lowering annual depreciation, improving cash flow, and mitigating of risk are some of the benefits associated with extending asset life.
Every stage of the asset lifecycle requires a strategic financial approach. From the initial acquisition to the ongoing operating expenses, to the replacement or upgrade of the existing asset. Understanding each stage of the asset lifecycle is vital in making informed capital budgeting decisions.
Managing assets well is crucial for organizations to succeed long-term and thrive in a competitive environment. Managing each stage of an asset’s life helps organizations use resources better. It also improves efficiency, increases return on investment, and reduces risk.
5 Key Strategies to Prolong your Asset Life
1) Regular Maintenance and Monitoring
Implementing a proactive asset maintenance plan and routine inspections will allow for early detection of wear and tear. This will prevent minor issues evolving into major ones, decreasing the asset lifespan, and increasing maintenance costs to the organization.
2) Asset Upgrades
Keeping the organizations assets up to date with the latest industry advancements may be beneficial in improving the performance of the assets. Components of a system may be upgraded, which can enhance and extend the asset’s functionality. Implementing an upgrade may prevent the early replacement of an asset, which can be more cost effective for an organization.
3) Lifecycle Cost Analysis
Regularly analyzing the cost-effectiveness of maintaining an asset versus replacing it will enable an organization to make better informed asset management decisions. Through regular lifecycle cost analysis, action can be taken at the appropriate time.
4) Knowledge Transfer
It is critical to keep documentation about all assets up to date. All information about an asset’s history, maintenance, and operation should be documented to allow easy knowledge transfer.
5) Employee Training
Investing in employee training is an important contributor to prolonging asset lives. Providing ongoing training to employees who operate the assets is important to increasing their usefulness. Workers need to know about improvements and best ways to use assets safely and efficiently.
Effective Asset Life Cycle Management
Effective Asset Lifecycle Management is a critical component of successful business operations. It entails managing the entire lifecycle of assets, from their acquisition to their disposal or retirement. This includes planning, tracking, maintaining, and disposing of assets in a way that maximizes their value and minimizes risks.
By effectively managing the entire lifecycle of assets, businesses can optimize their use, reduce costs, improve efficiency, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. Implementing strategic stages of asset lifecycle management involves various processes. These processes include asset procurement, asset tracking and monitoring, preventative maintenance and repairs, and asset disposal or retirement planning.
Maximize your Asset Lifecycles with Asset Management Software
The asset lifecycle is a complex journey that requires proper planning and management to achieve long-term success. IQX Asset Management Software provides asset managers with the tools they need to navigate the asset lifecycle journey. From initial acquisition to retirement, IQX helps organizations to create, manage, and optimize their assets and to maximize their return on investment. With an easy-to-use interface and powerful features, IQX Asset Management Software provides users with the ability to manage the entire lifecycle of their fixed assets.
From asset creation to transfers and disposals, users have the ability to monitor and manage their assets throughout their entire lifecycle. IQX Asset Management Software provides users with the ability to review their asset portfolios and take proactive steps to ensure that their assets remain in optimal condition. IQX Asset Management Software is the ideal solution for organizations looking to navigate the asset lifecycle journey for long-term success.
Related Posts
If you enjoyed reading this, then please explore our other articles below:




